Blue Whale
CLASS: Mammalia
ORDER: Cetacea
SUBORDER: Mysticeti
FAMILY: Balaenopteridae
GENUS: Balaenoptera
SPECIES: musculus
The blue whale is one of the rorquals, a family that also includes the humpback whale, fin whale, Bryde's whale, sei whale, and minke whale. On land an animal the size of a blue whale would be crushed by its own weight without the support of large heavy bones. Because its body is supported by water, as a sea animal, the need for heavy bones to support its weight disappeared. This, plus the availability of a large food supply, have made it possible for the blue whale to reach such an enormous size. The blue whale makes deep and rumbling sounds which can be felt as much as heard. These low-frequency sounds travel long distances through water, allowing blue whales to communicate with each other over hundreds of miles of ocean.
Physical Description
The blue whale is the largest mammal, possibly the largest animal, to ever inhabit the earth. Its body is long, somewhat tapered, and streamlined, with the head making up less than one-fourth of its total body length. Its rostrum (upper part of the head) is very broad and flat and almost U-shaped, with a single ridge that extends just forward of the blowholes to the tip of the snout. Its blowholes are contained in a large, raised "splash guard", and the blow is tall and straight and over 20 feet (6 meters) high. Its body is smooth and relatively free of parasites, but a few barnacles attach themselves to the edge of the fluke and occasionally to the tips of the flippers and to the dorsal fin. There are 55-68 ventral grooves or pleats extending from the lower jaw to near the navel.

Surface Characteristics
Color
The blue whale is blue-gray in color, but often with lighter gray mottling on a darker background (or with darker spots on a lighter background). The underside of its flippers may be a lighter color or white, while the ventral (underside) of the fluke is dark. The blue whale acquires microorganisms called diatoms in the cold waters of the Antarctic and North Pacific and North Atlantic which give the underside of its body a yellowish green caste. Because of this yellow color, the early whalers gave it the name "sulfur bottom."
Fins and Fluke
Its dorsal (top) fin is small and triangular or falcate (curved) in shape, and is located three-fourths of the way back on the body. The fin measures only one foot (30 cm) at its highest point though its size and shape are highly variable. Its flippers are tapered and relatively short, about 12% of the total body length. The flukes are broad and triangular. The rear edge is smooth with a slight median notch.
Length and Weight
The longest blue whale ever recorded was a 108-foot adult female caught during whaling efforts in Antarctica! In modern times, blue whales in the Southern Hemisphere reach lengths of 90-100 feet , but their Northern Hemisphere counterparts are smaller, on average 75 to 80 feet (23 to 24.5 m). Blue whales can weigh over 100 tons (99,800 kg). Females are larger than males of the same age, the largest perhaps weighing as much as 150 tons (136,000 kg).
Feeding
The blue whale is thought to feed almost exclusively on small, shrimp-like creatures called euphausiids or krill. During the summer feeding season the blue whale gorges itself, consuming an astounding 4 tons (3.6 metric tons) or more each day. This means it may eat up to 40 million krill a day. As a baleen whale, it has a series of 260-400 fringed overlapping plates hanging from each side of the upper jaw, where teeth might otherwise be located. These plates consist of a fingernail-like material called keratin that frays out into fine hairs on the ends inside the mouth near the tongue. The plates are black and measure about 20 inches (51 cm) in length toward the front of the mouth and about 40 inches (102 cm) at the rear. During feeding, large volumes of water and food can be taken into the mouth because the pleated grooves in the throat expand. As the mouth closes water is expelled through the baleen plates, which trap the food on the inside near the tongue to be swallowed.
Mating and Breeding
Recent research indicates that blue whales reach sexual maturity between the ages of 6-10 years, or when males average about 74 feet (23 m) and females are about 79 feet (24 m). Calves are born at intervals of 2 to 3 years and gestation is about 12 months. Calves are 23 to 27 feet (7-8.2 m) long at birth and 3 tons (2,722 kg). Calves nurse for 7 to 8 months and are weaned when they reach 52 feet (16 m) in length. At that time they weigh about 23 tons (20,900 kg). During the nursing period, calves consume 100 gallons (379 liters) of the fat-rich mother's milk each day, gain 200 pounds a day, or 8 pounds an hour, and grow 1 and 1/2 inches in length a day.
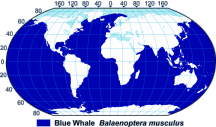
Range Map
Distribution and Migration
Blue whales may be found in all oceans of the world. They migrate to tropical-to-temperate waters during winter months to mate and give birth to calves. They can feed throughout their range, in polar, temperate, or even tropical waters.
Natural History
Though they may be found singly or in small groups, it is more common to see blue whales in pairs. They are sometimes seen in larger groups and loosely defined concentrations of 50-60 have been observed. They are fast, strong swimmers, capable of reaching 30 mph (48.3 km/hr) when alarmed, but they usually cruise along at about 12 mph (19.3 km/hr).
Status
Because of their enormous size and speed, blue whales were safe from early whalers, who could not pursue them in open boats with hand harpoons. But in 1868 a Norwegian, Sven Foyn, revolutionized the whaling industry with the invention of the exploding harpoon gun and by using steam and diesel powered factory ships and catcher boats. He also perfected the technique of inflating dead whales with air so they wouldn't sink after being harpooned. The whaling industry began to focus on blue whales after 1900. A single 90-foot blue whale could yield up to 120 barrels of oil, and the blues were killed by the thousands. The slaughter peaked in 1931 when over 29,000 were killed in one season. After that blue whales became so scarce that the whalers turned to other species and, belatedly, the International Whaling Commission (IWC) banned all hunting of blue whales in 1966 and gave them worldwide protection. Recovery has been extremely slow, and only in the last few years have there been signs that their numbers may be increasing. Pre-whaling population estimates were over 350,000 blue whales, but up to 99% of blue whales were killed during whaling efforts. Presently, there are an estimated 5-10,000 blue whales in the Southern Hemisphere, and only around 3-4,000 in the Northern Hemisphere.
Bibliography
- Bartolotti, D. 2008. Wild Blue: A Natural History of the World's Largest Animal. St. Martin's Press.
- Calambokidis, J. and G.H. Steiger. 1997. Blue Whales.. Worldlife Series Library. Voyager Press, MN.
- Sears, R. 2002. Blue Whale, Balaenoptera musculus. - In: Encyclopedia of marine mammals (W.F. Perrin, B. Wursig, and J.G.M. Thewissen, eds). Academic Press, San Diego, CA. pp.112-116.
- Small, G.L. 1971. The Blue Whale. Columbia University Press.
Acknowledgements
We greatly appreciate the knowledge and assistance of John Calambokidis of Cascadia Research, who contributed to the revision of this fact sheet. Illustrations courtesy Uko Gorter, copyright © 2017 all rights reserved.
FACT SHEETS MAY BE REPRINTED FOR EDUCATIONAL OR SCIENTIFIC PURPOSES
|



